Ultrananaotech, ULTRANANOTECH
The Power Behind Lithium-Ion Batteries: A Modern Marvel
In today’s fast-paced world driven by technology and innovation, few innovations have been as transformative as the lithium-ion battery and are bringing new dimension in renewable energy. From smartphones to electric vehicles (EVs), these rechargeable powerhouses have revolutionized portable electronics and are now leading the charge towards a greener future in transportation. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of lithium-ion batteries, exploring their structure, function, and impact on various industries.
Structure and Components:
At its core, a lithium-ion battery consists of several key components:
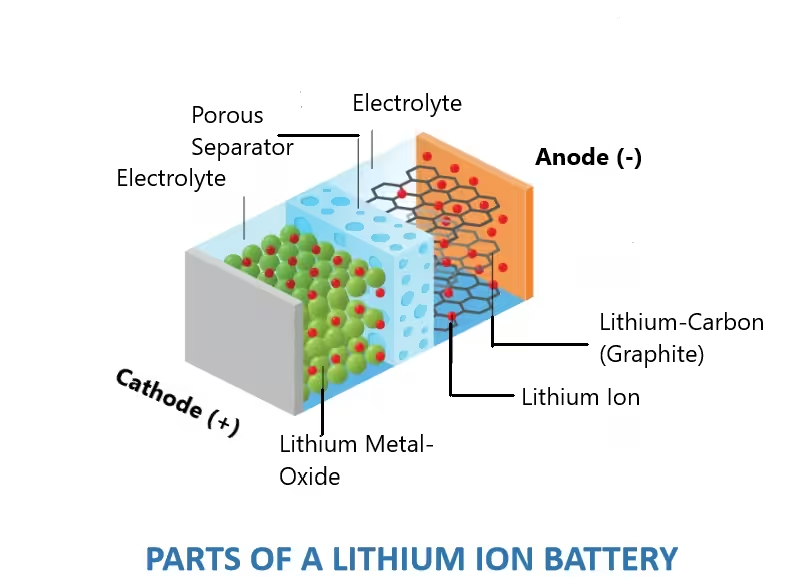
Cathode: This is typically made of lithium metal oxides, such as lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2), lithium manganese oxide (LiMn2O4), or lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4). The cathode’s composition influences the battery’s performance and stability.
Anode: Usually made from carbon graphite, the anode stores lithium ions during charging. Graphite is chosen for its ability to intercalate lithium ions between its layers, enabling reversible charging and discharging. Charging and discharging is the core of performance of Lithium-ion battery.
Electrolyte: A conductive solution or gel that allows lithium ions to move between the cathode and anode during charge and discharge cycles. It is typically a lithium salt dissolved in an organic solvent.
Separator: A permeable membrane that physically separates the cathode and anode while allowing lithium ions to pass through. It prevents short circuits by keeping the electrodes apart. Generally, they are made up polymeric materials.
Working Principle:
During charging, lithium ions move from the cathode through the electrolyte to the anode, where they are stored. When discharging, these ions move back through the electrolyte to the cathode, generating electrical current that powers devices.
Applications and Impact
Consumer Electronics:
Lithium-ion batteries have made portable electronics truly mobile. They power smartphones, laptops, tablets, and wearable devices, offering high energy density and long-life cycles compared to earlier battery technologies. Lithium ion battery is considered as a power house for Renewable Energy

Fig: Representation of Lithium Ion Battery
Electric Vehicles (EVs):
The automotive industry is increasingly adopting lithium-ion batteries due to their superior energy density and ability to provide extended driving ranges. EVs powered by lithium-ion batteries contribute significantly to reducing greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional combustion engines.
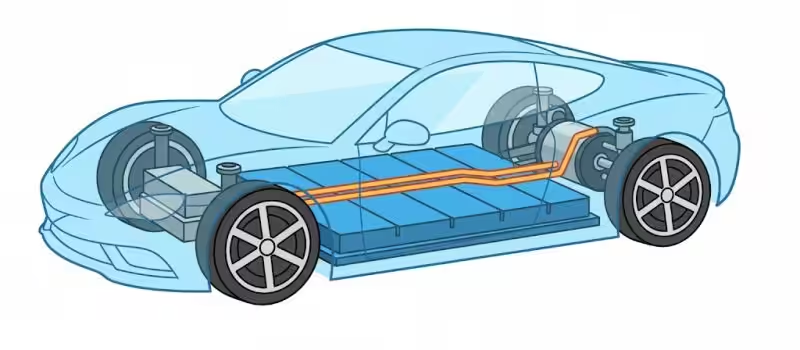
Fig: Electric vehicle with lithium ion battery
Energy Storage:
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind are intermittent, making energy storage crucial for grid stability. Lithium-ion batteries store excess energy during times of low demand and release it when needed, helping balance supply and demand.

Fig: Lithium Ion Energy Storage
Challenges and Future Developments
While lithium-ion batteries have transformed multiple industries, they are not without challenges:
Safety Concerns: Issues like thermal runaway (where batteries overheat and catch fire) have been reported, prompting ongoing research into safer battery designs. Research community working round the clock to address the safety concern. More adaptability will come if all safety concerned are get addressed
Cost: Despite advancements, lithium-ion batteries remain expensive, particularly for large-scale applications like grid storage. Need cost effective solution to commercialized in large scale.
Resource Availability: Lithium, cobalt, and nickel are key materials in these batteries, and their sustainable sourcing remains a concern.
Future Developments:
Researchers are exploring alternative materials for electrodes and electrolytes to improve battery performance, safety, and sustainability. Solid-state batteries, which replace liquid electrolytes with solid conductors, show promise in addressing safety and energy density concerns.
In essence, the journey of the lithium-ion battery is not just about energy storage—it’s about powering progress itself.
Courtesy of: Simran Jain, Technical sales executive at ULTRANANOTECH PVT LTD