ULTRANANOTECH, Uncategorized
Fuel Cell and Its Importance
Fuel cell is a device that generates electricity through an electrochemical reaction. Fuel cell uses the chemical energy of hydrogen or other fuels to cleanly and efficiently produce electricity. In the case of hydrogen fuel cell, hydrogen is the source of fuel and the only products are electricity, water, and heat. Fuel cells do not need to be periodically recharged like batteries, but instead, continue to produce electricity as long as a fuel source is provided.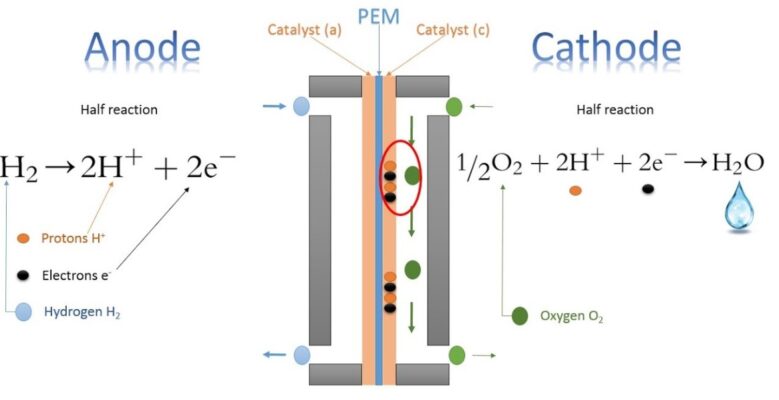
Scheme: A Schematic presentation of fuel cell reaction
A fuel cell is composed of an anode, cathode, catalyst, and electrolyte membranes sandwiched between two electrodes. Oxygen from the air passes over one electrode and hydrogen over the other, generating electricity, water, and heat. In a hydrogen fuel cell, a catalyst at the anode separates hydrogen molecules into protons and electrons, which take different paths to the cathode. The electrons go through an external circuit, creating a flow of electricity. The protons migrate through the electrolyte to the cathode, where they unite with oxygen and electrons to produce water and heat. Bipolar plates on either side of the cell help to distribute gases and collect the electrical current.
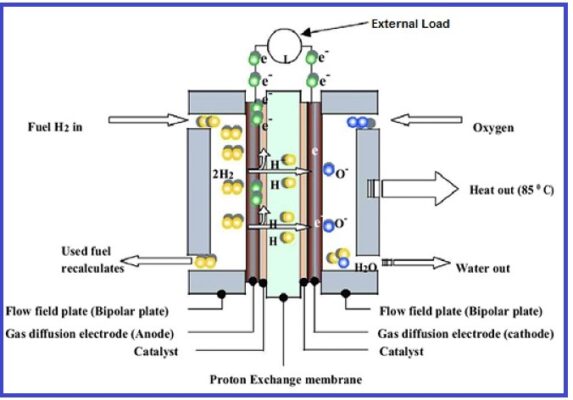
Representative Sketch of PEMC Fuel Cell Assembly
In some cases, Fuel cell produce very less voltage which may not be sufficient for most of the application. In those cases, stacking of fuel cells is required to increase the voltage and hence performance. Individual fuel cells can be collected into a unit and connected to each other in series, resulting in a “stack” of cells that can generate more voltage.
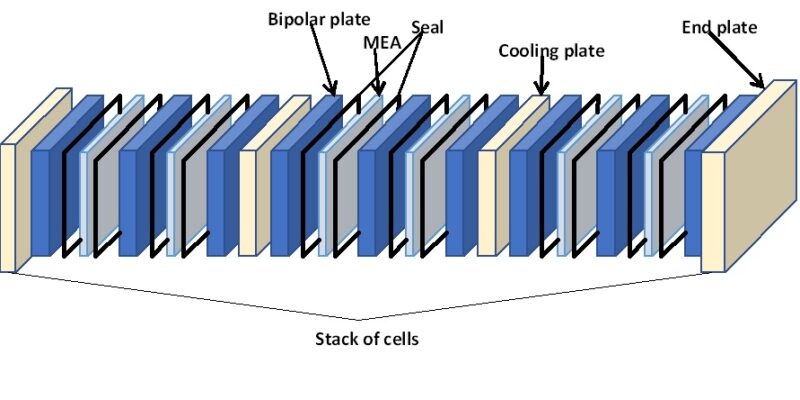
Representative picture of Fuell Cell Stack
Fuel cells have a number of advantages which includes:
- High efficiency
- Quick refueling
- Quiet operation
- Compact size
- Rapid response to changes in electrical demand
- Long lifetimes
- Longer ranges, are increasingly important for larger, heavier vehicles.
- lower or zero emissions
- high power density
Fuel cells have several benefits over conventional combustion-based technologies currently used in many power plants and vehicles.
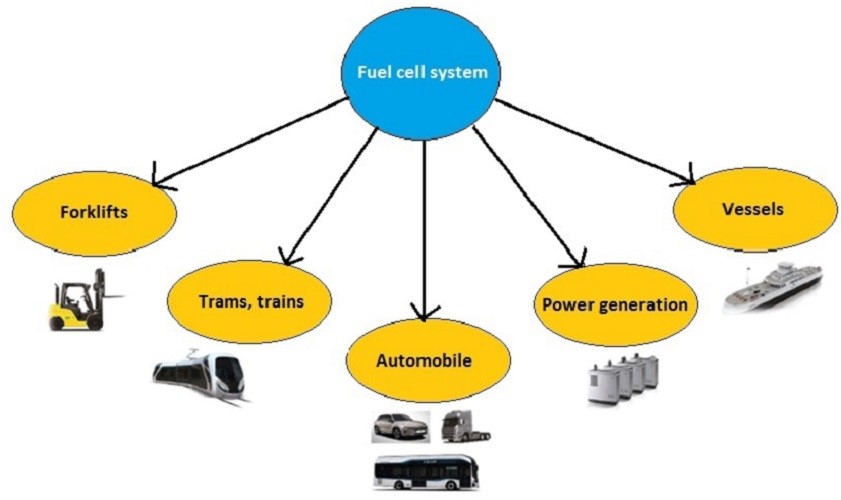
Fuel cell can be used in a lot of applications, which includes warehouse logistics, global distribution, utility vehicles, buses, scooters, bicycles, trains, stationary power generation, boats and submarine, and many more. Fuel cells are lightweight, long-lasting, and portable power sources that can be used in backup power applications.
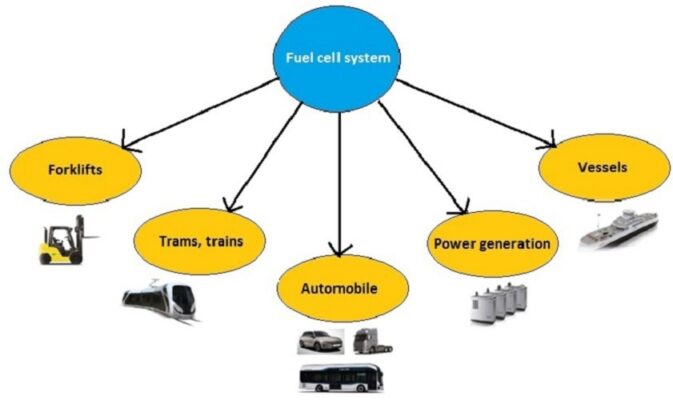
Figure: Representing various applications of fuel cell
COURTESY: ULTRANANOTECH PVT. LTD
For more information visit us at: https://ultrananotec.com/
 +91-8800903073, 8452810712
+91-8800903073, 8452810712